[HCI] L2-6. Mental Models and Representations
Table of Contents
Mental Model

- Mental Model : An internal, simulatable understanding of external reality
- Using mental models we generate expectations or predictions about the world
- and then we check whether the actual outcomes match our mental model
-> When reality doesn’t match with our mental model, it makes us uncomfortable
How to do things good?

- 2 Ways of users' mental model in our systems match the way our systems actually work
- Designing systems that act the way the user expects them to act
- Designing systems that teach the user how they react
Mental Models and Education
-
Design interfaces = playing the role of an Educator
-
Goal : To teach user how the system works through the design of interface
-
Tactic : Have to design interfaces that teach users while they're using them
- Good representations shows the user exactly how the system actually works
-
Mental Model in Action

5 Tips : Mental Models for Learnable Interfaces

- Predictability
- Can the user predict what will happen?
- Synthesizablility
- User should be able to see the sequence of actions that led to their current state
- GUI 에서는 어려울 수 있음 -> 대신, undo menu에서 log of actions를 제공해 주는 방법 고려 가능
- CLI 에서는 자연스레 위 원칙이 잘 지켜짐
- Familiarity
- ~= Normans’ principle of Affordances
- The interface should leverage actions with which the user is already familiar from real-world experience
- Ex) 상태 표시 good/bad -> 초록/노랑(good), 파랑/노랑(bad)
- Generalizability
- ~= Normans’ principle of Consistency
- Knowledge of one user interface should generalize to others
- Ex) save, copy, paste 기능 -> 다른 interface와 비슷하게 동작하도록 디자인
- Consistency
-
!= Normans’ principle of Affordances
-
Similar tasks or operations within a single interface should behave the same way
- Ex) ctrl + X -> cut texts (텍스트 선택되었을 때) / close application (텍스트 선택없을 때) : BAD
-> '’By book Human-Computer Interaction by Dix, Finlay, Abowd, & Beale’‘
Representations

(Bad Representation)
(Good Representation)
- Representation : Internal symbols for an external reality
- The most powerful tool in our arsenal
- to help ensure users have effective mental models of our system
Representation for Problem Solving
Example(1)



- Representation took a hard problem an made it very easy
Example(2)

- Audio is a poor representation of complex problems
- FIRST, Write the problem out
- Written representation of the preblem
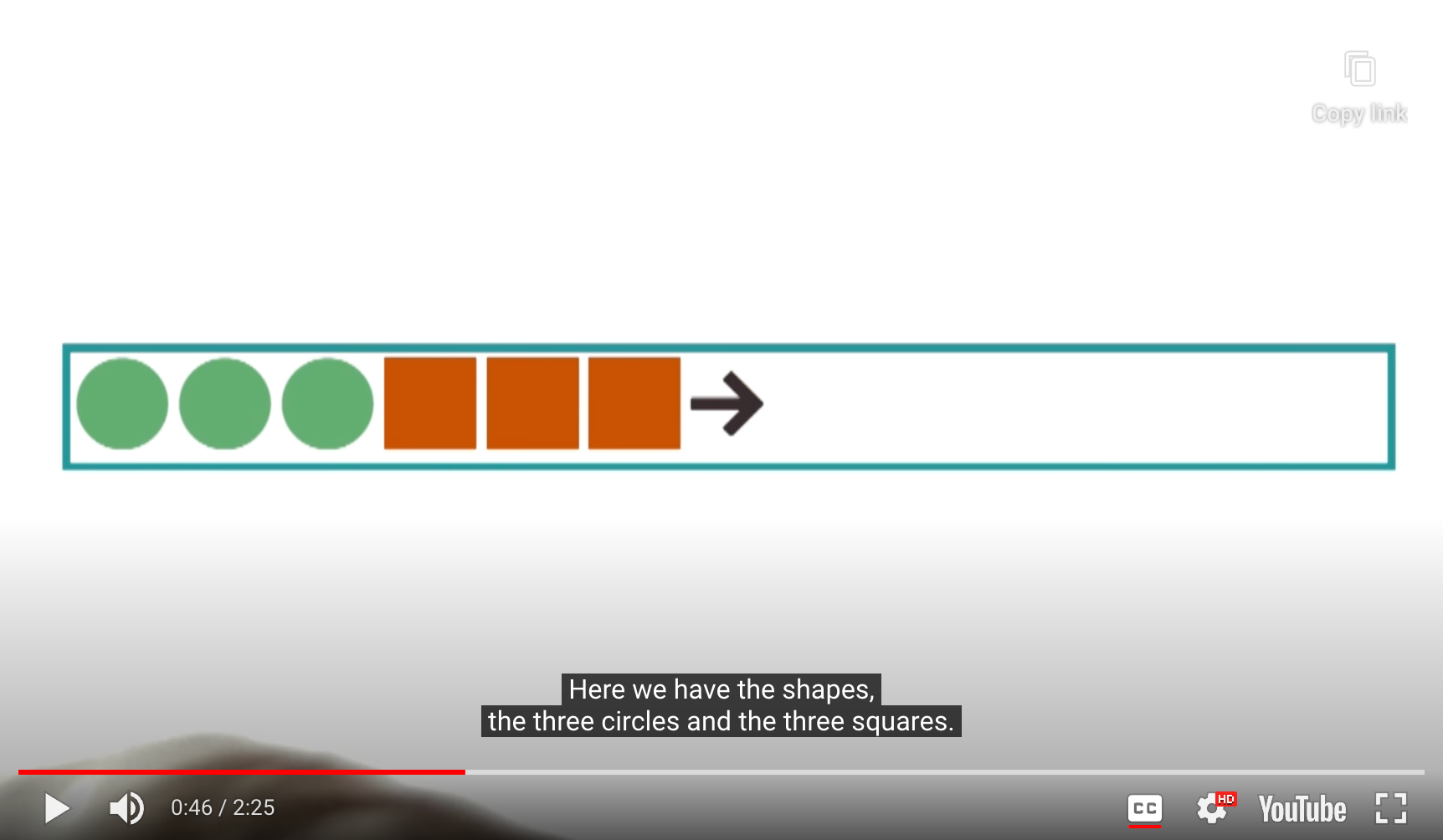
- Visual representation
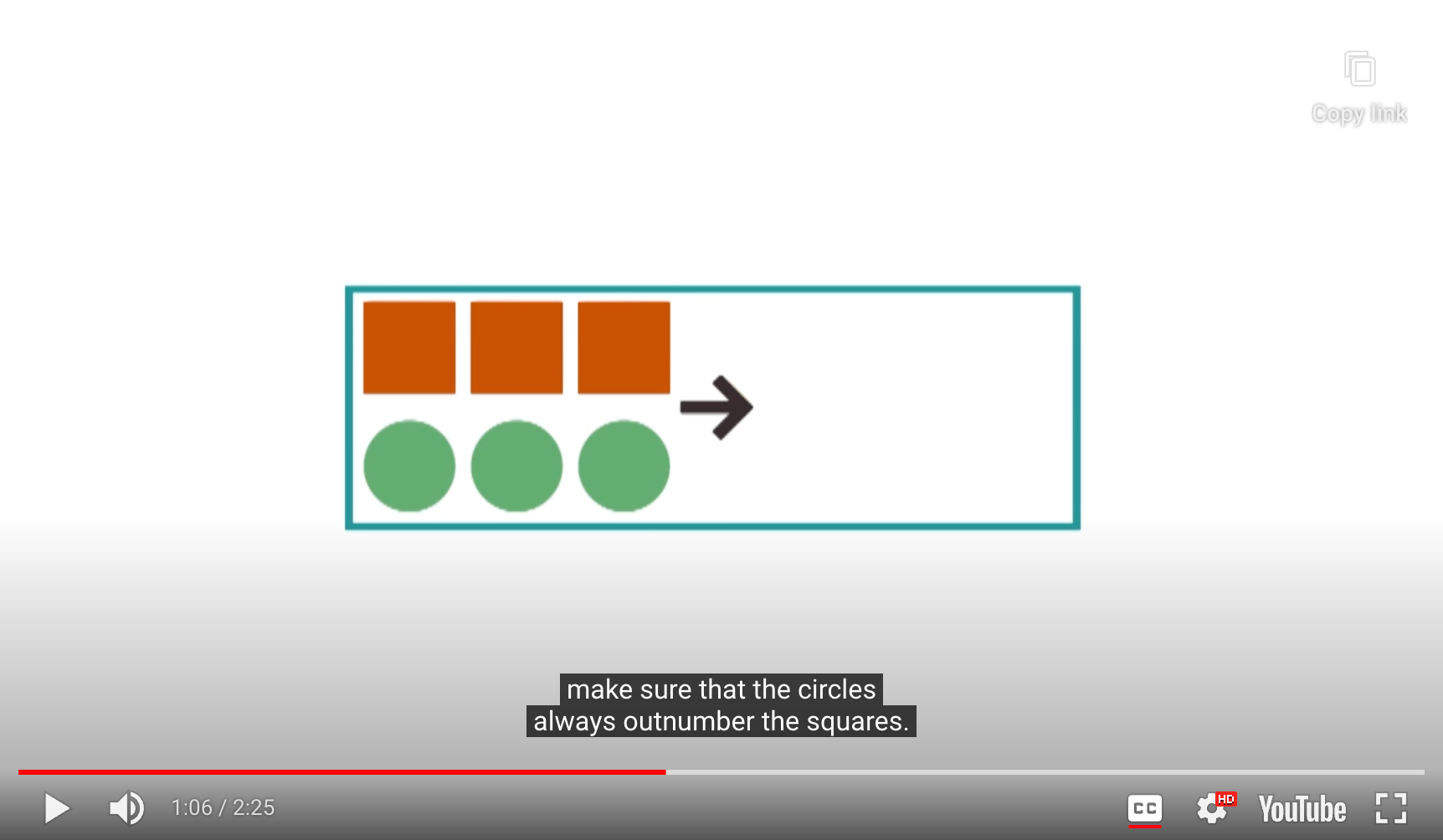
- Better representation
- Make sure that the circles always outnumber the squares
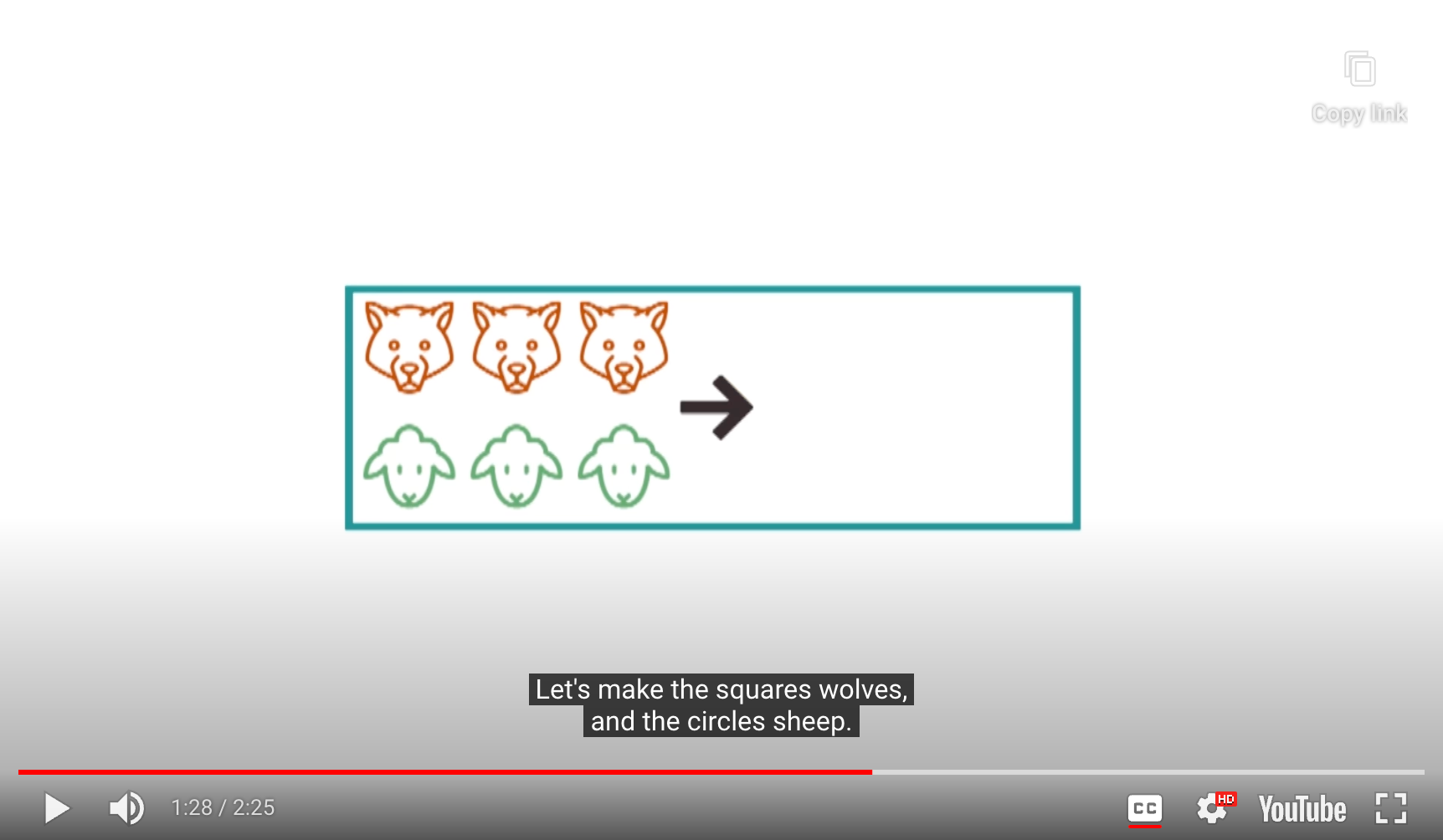
- Make it more self evident
- As long as the sheep outnumber the wolves, the sheep can defend themselves, kind of
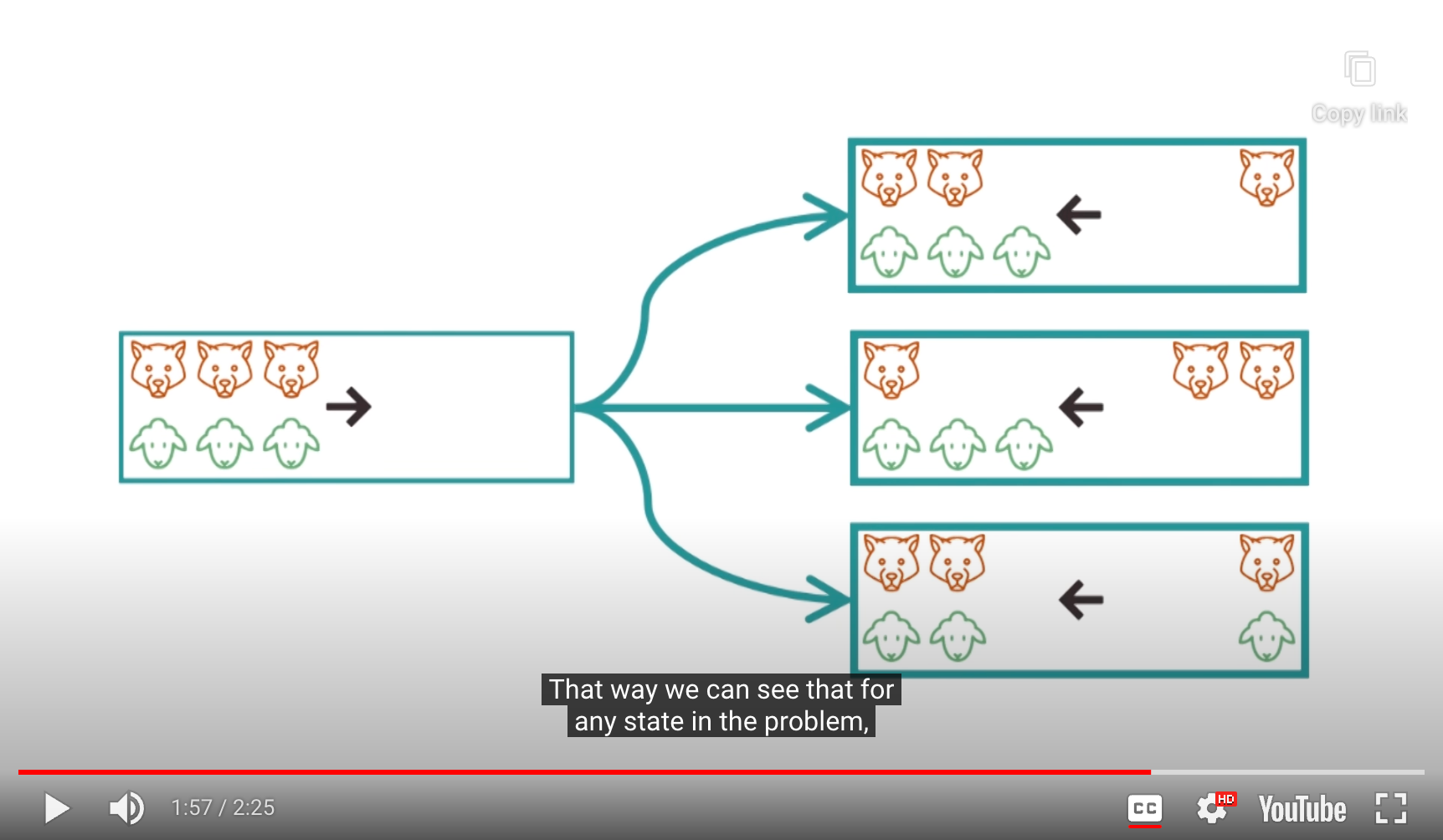
- Visualize a finite number of next legal states
- Allow us to notice when we’ve accidentally revisitied in earlier states
- Characteristics of Good Representations
Representations in Interfaces
- Google Calendar
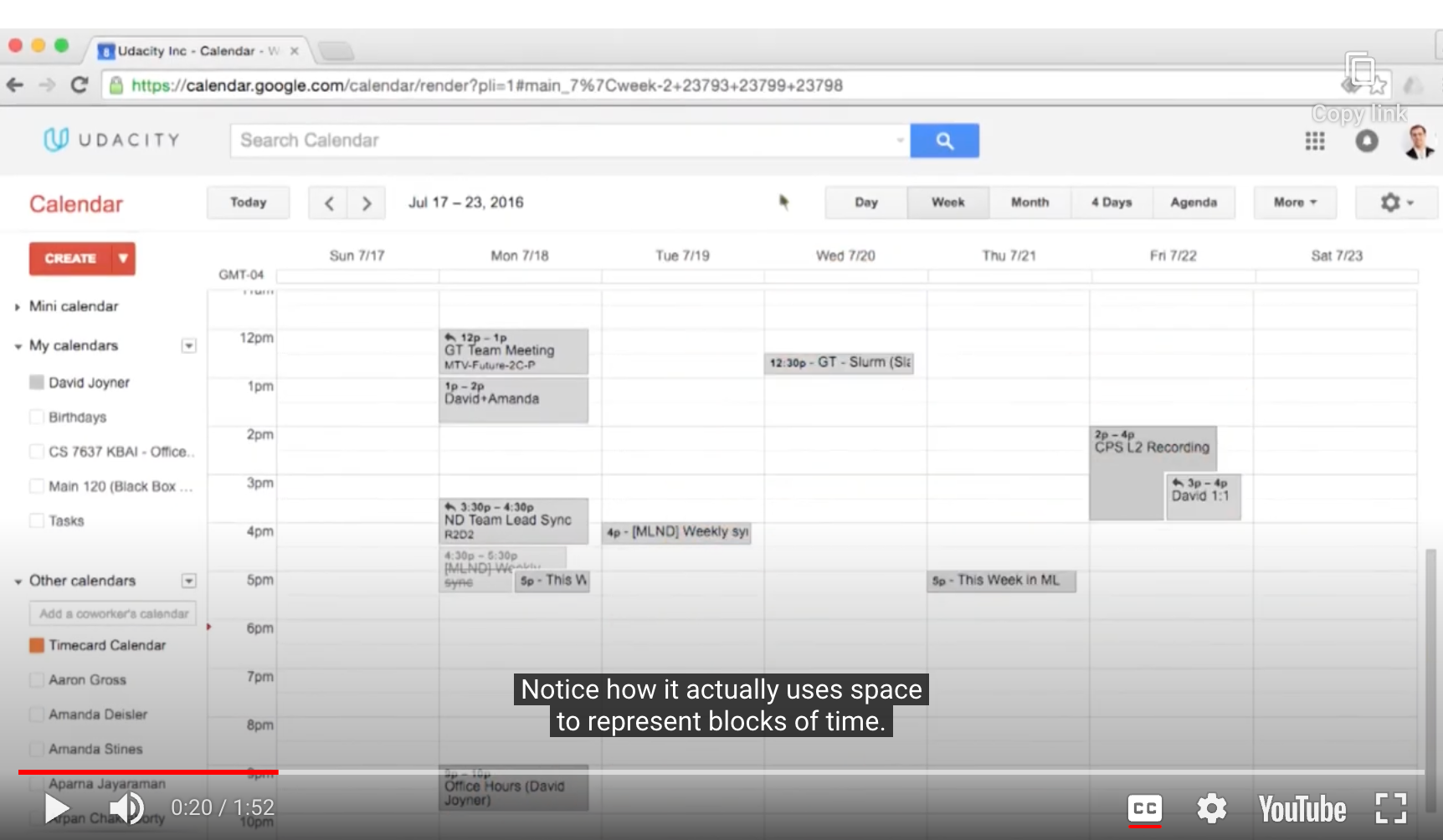
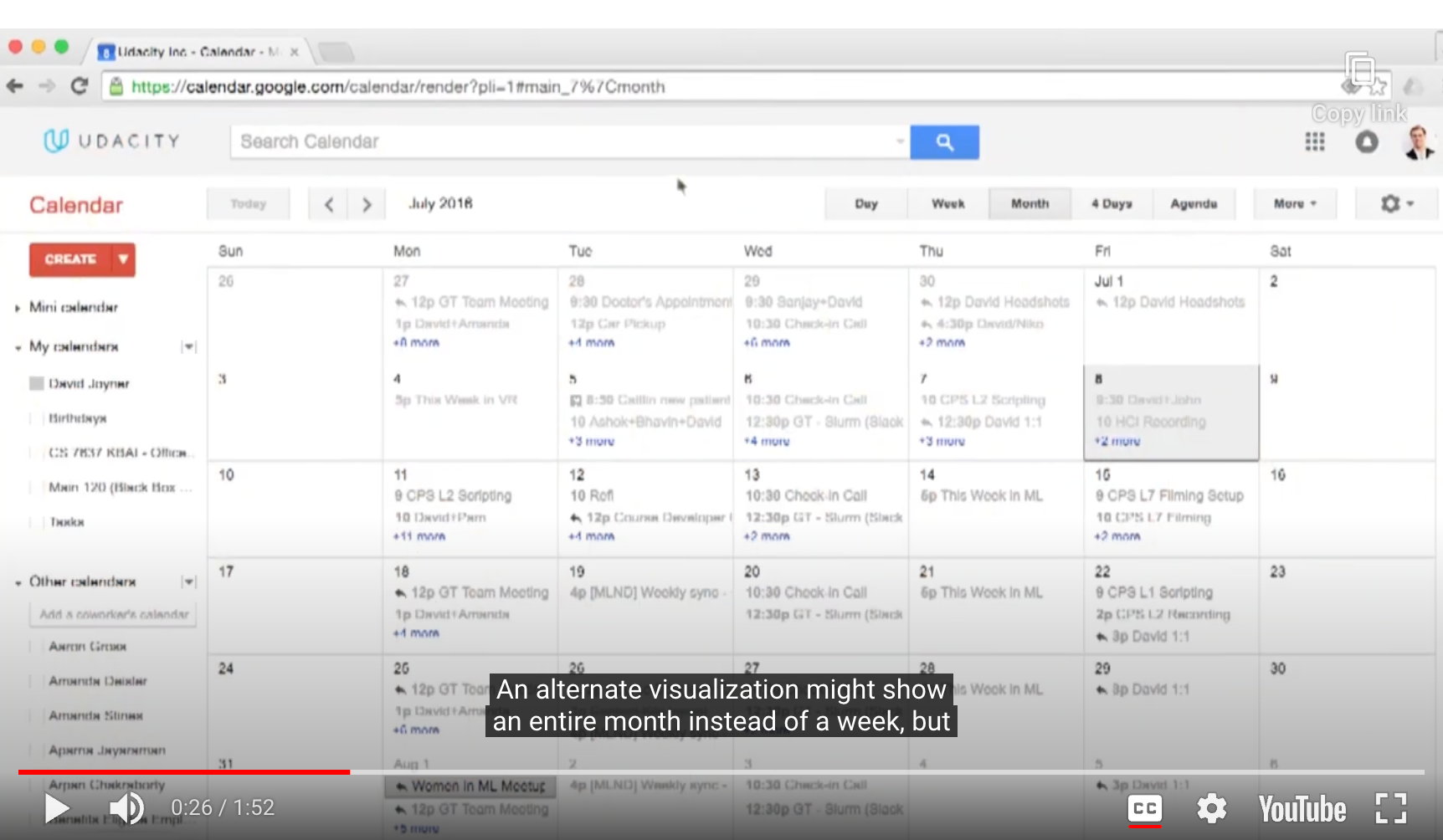
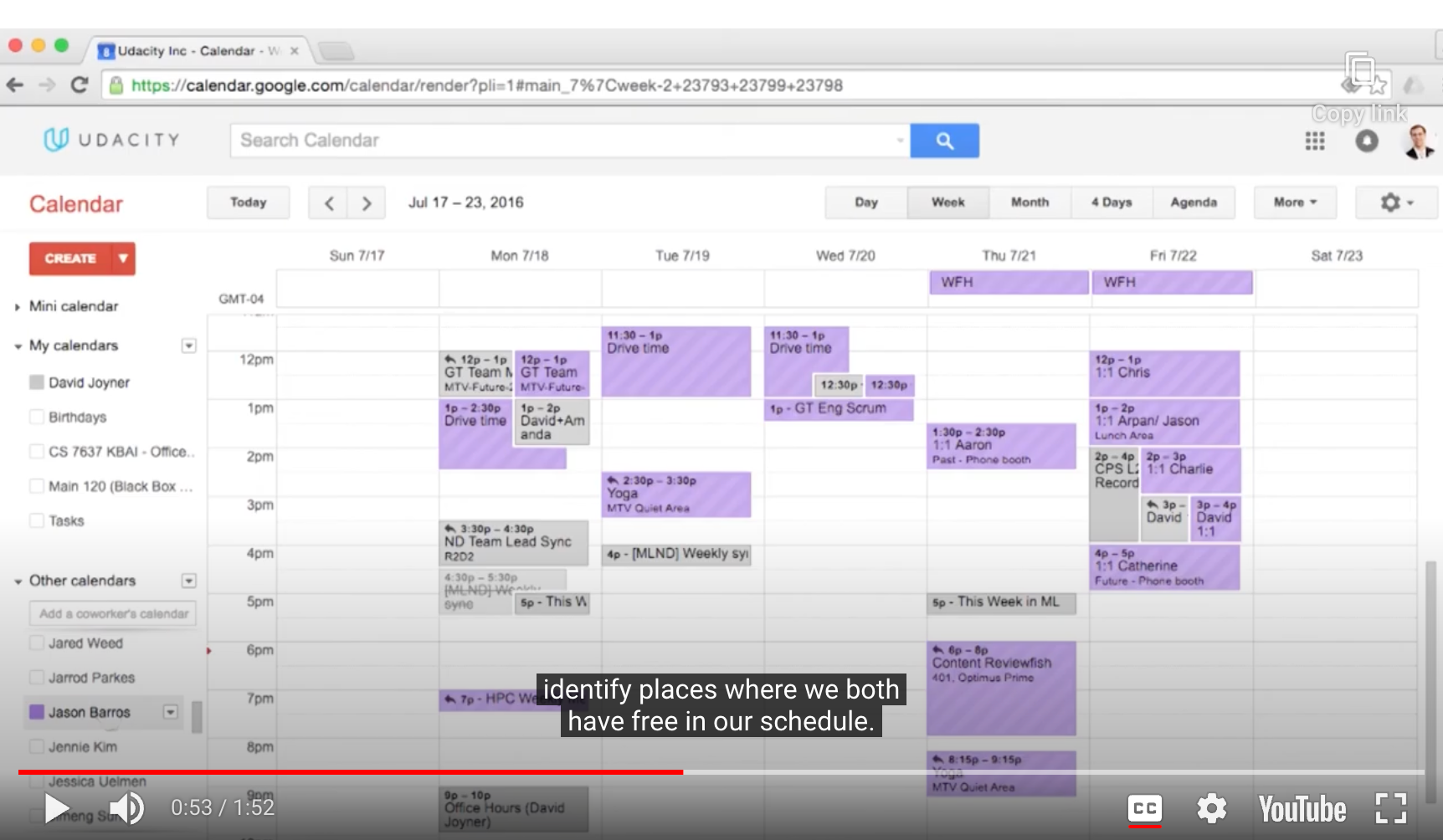
(다른 사람과 일정이 잘 맞는지도 알 수 있음)
- PowerPoint
Keep in Mind…
- Representations when used correctly can make many tasks trivial, or even invisible
Metaphors and Analogies

- Wall Street Journal 웹 사이트 - leverage an ‘Analogies’ to print edition
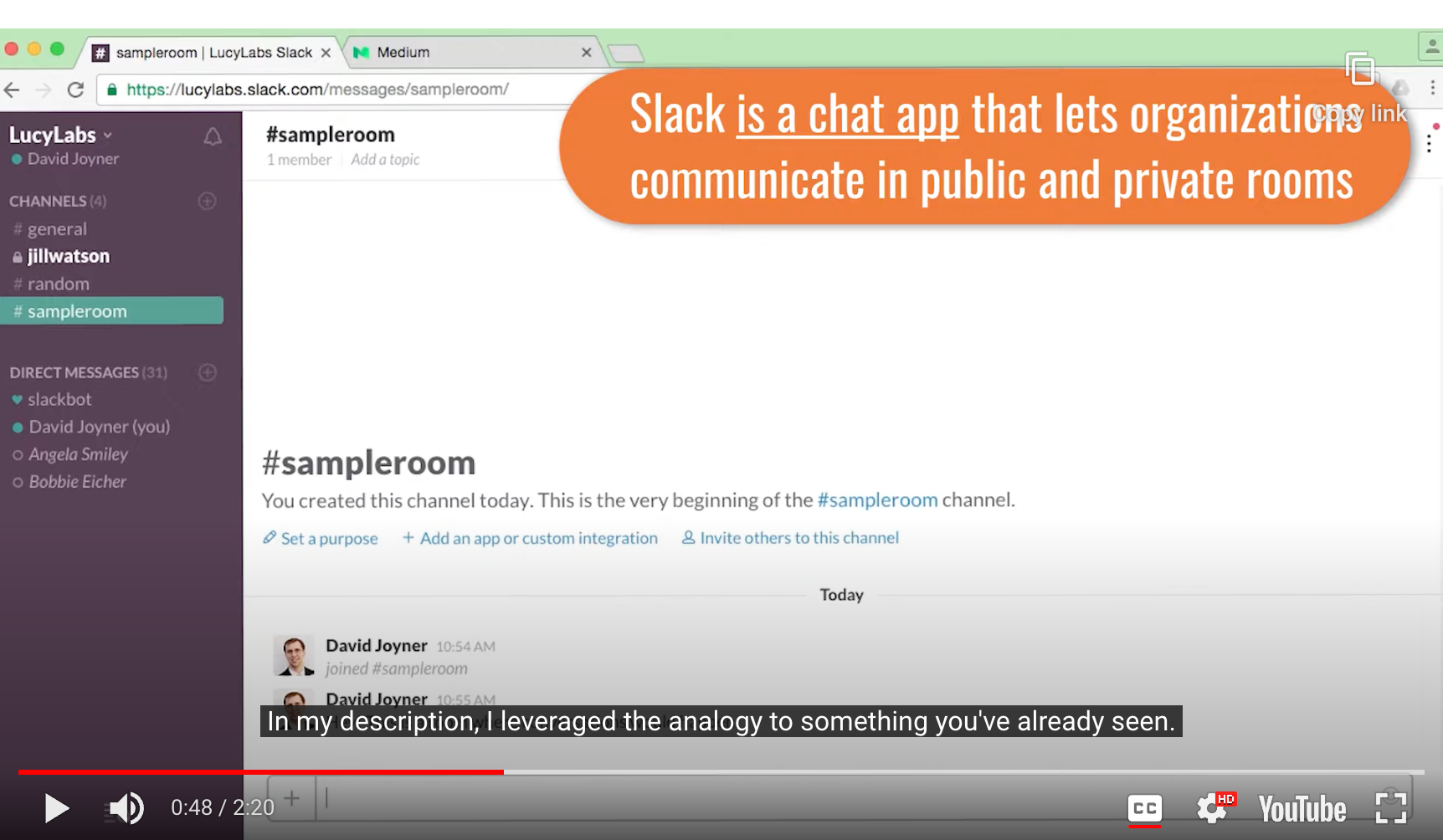
- Slack - ‘chat app’ Analogies
- WordPress + Huffington Post + Facebook ‘Analogies’
-> When you use analogies to other interfaces, users may not know where the analogy ends
Exploring HCI: Metaphors and Analogies

- Full keyboard - mobile phone keyboard

- Remember!
- Analogies make the interface more learnable, but they may restrict the interface to outdated constraints


Design Priciples Revisited
- Interface를 사용할 때 사람들이 Analogy 나 Metaphor 를 활용하여 추론(reason)하는 이유는
- ‘Consistency’ Principle이 그만큼 중요하기 때문!
- Interface가 시스템을 어떻게 사용해야 할지 사용자에게 가르쳐야 하는 이유는
- ‘Affordance’ Principle과 연관됨
- 시스템이 보여지는 방식이 사용자에게 어떻게 사용해야 할지 알려주어야 하기 때문
- ‘Affordance’ Principle과 연관됨
- Representation이 중요한 이유는
- ‘Mapping’ Principle과 연관됨
- Interface와 task가 그 자체로(at-hand) 연결되어야 하기 때문
- 좋은 representation은 사용자가 interface 상의 actions - 실제 outcomes 사이의 mapping을 예상하게 해 줌
- ‘Mapping’ Principle과 연관됨
Learning Curves
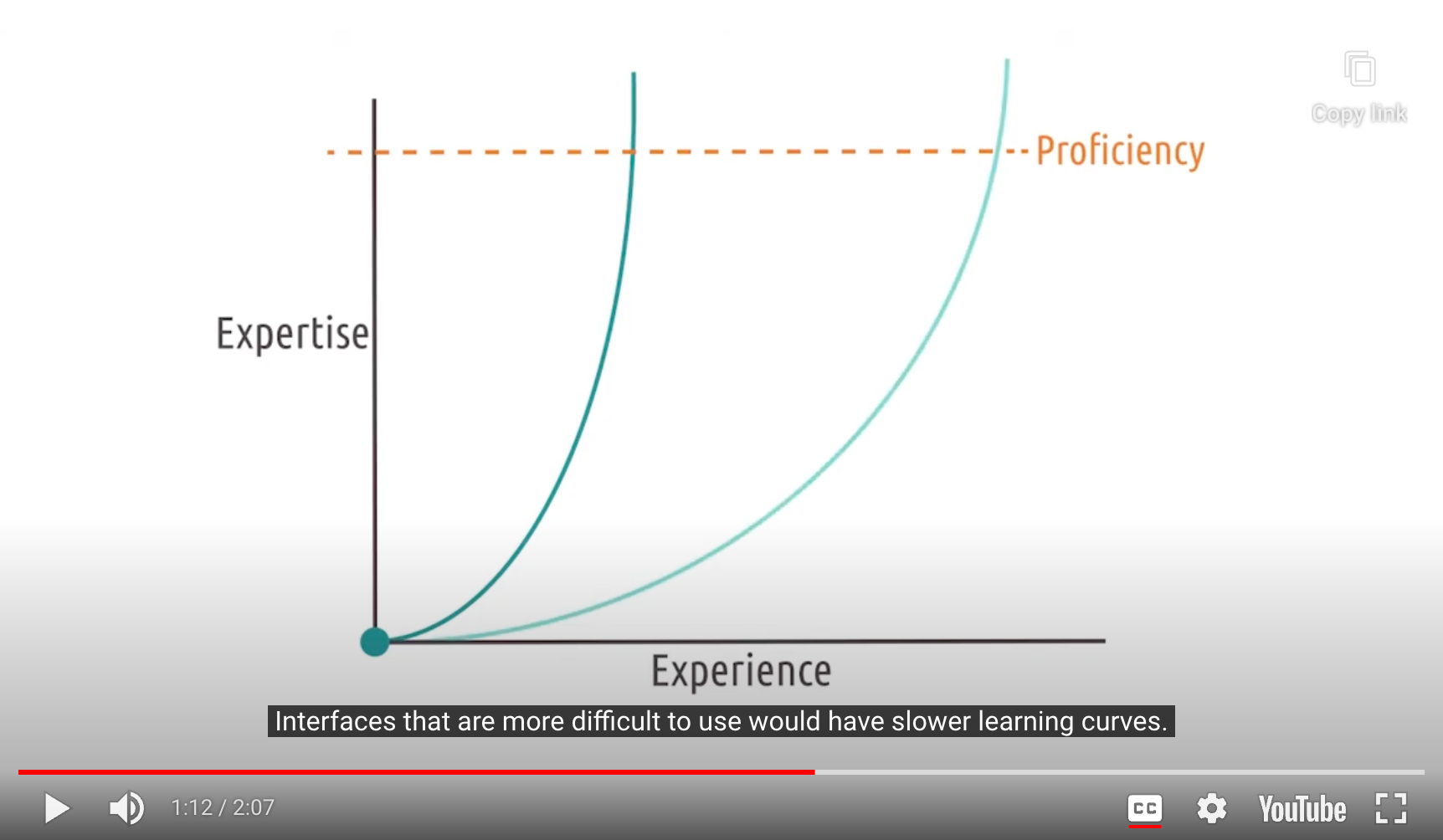
- Steep/Rapid learning curves <-> Slower learning curves
- 어떻게 향상시킬 수 있을까?
- By Metaphors and Analogies
- 어떻게 향상시킬 수 있을까?
User Error: Slips and Mistakes

- As designers : There is really no such thing as User Error
- Any user error is a failure of the interface to properly guide the user to the right action
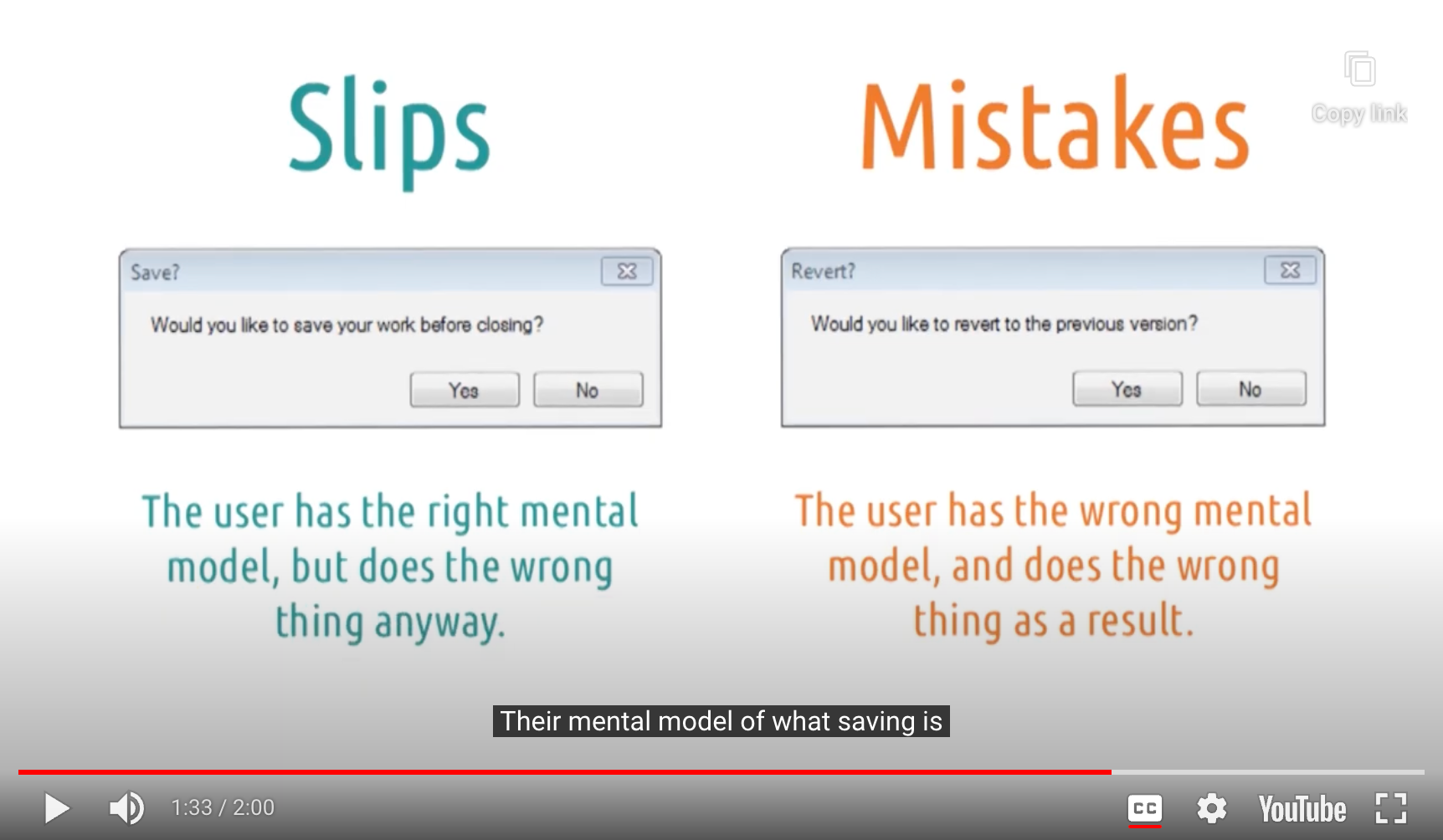
- Slips
- ex) Yes-No 버튼 위치가 바뀌어 있거나 / 기본이 No라서 Enter를 눌렀을 때 저장이 안되거나
- Mistakes
- ex) revert의 뜻을 대부분의 사용자는 모른다 / 몰라서 No를 선택하면 작업한 결과물을 영영 잃어버린다
2 Types of Slips
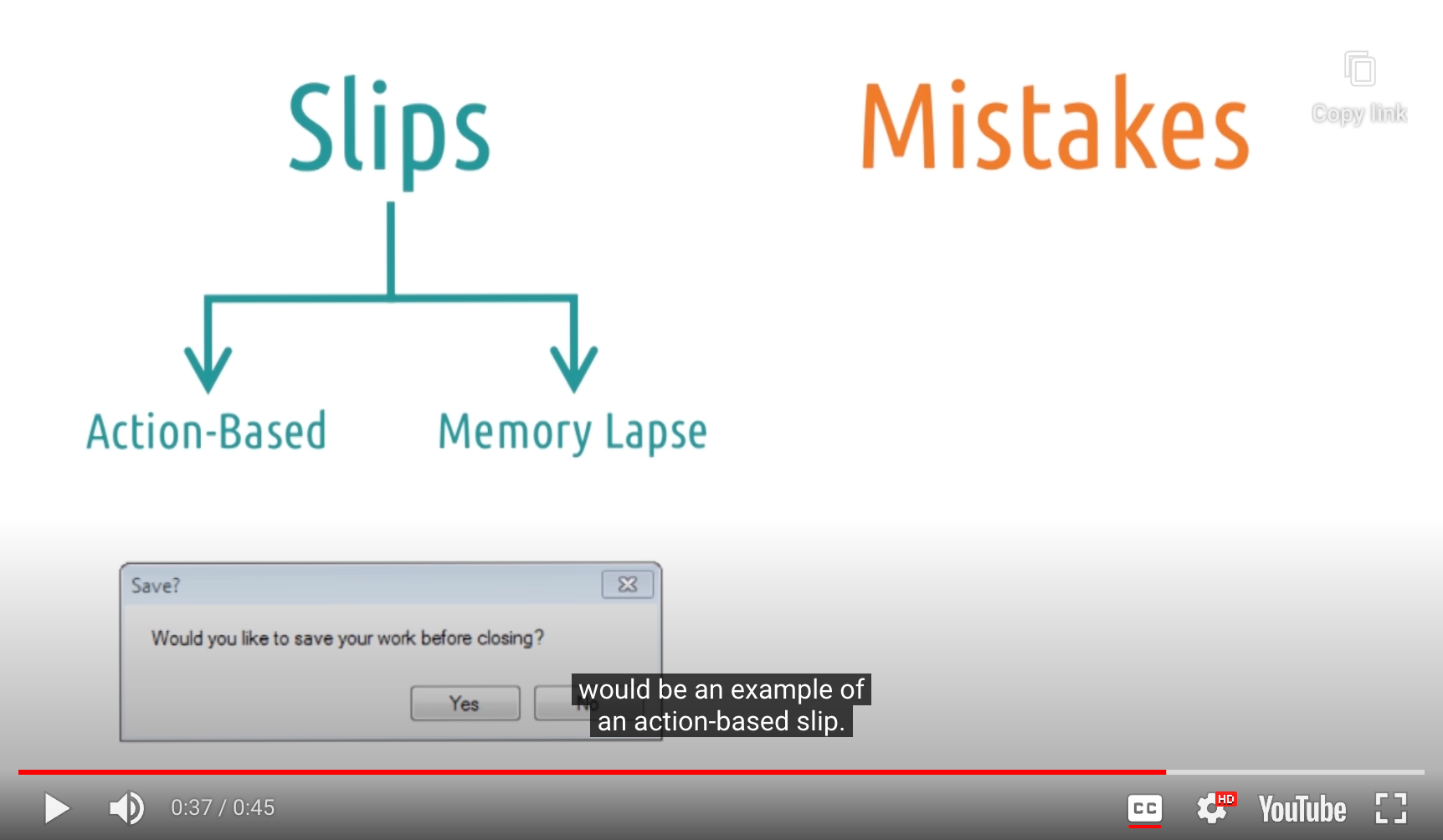
- Action-Based : Doing the wrong thing
- 올바른 action을 알고 있음에도, 사용자가 잘못된 action을 수행하거나, 잘못된 대상에 올바른 action을 사용할 경우
- Yes 대신 No 를 클릭함
- 올바른 action을 알고 있음에도, 사용자가 잘못된 action을 수행하거나, 잘못된 대상에 올바른 action을 사용할 경우
- Memory Lapse : Forget to do the right thing
- 어떻게 하는지 알고 있지만, 잊어버리는 경우
- 오븐에서 타이머 설정을 안함
- 어떻게 하는지 알고 있지만, 잊어버리는 경우
2 Types of Mistakes
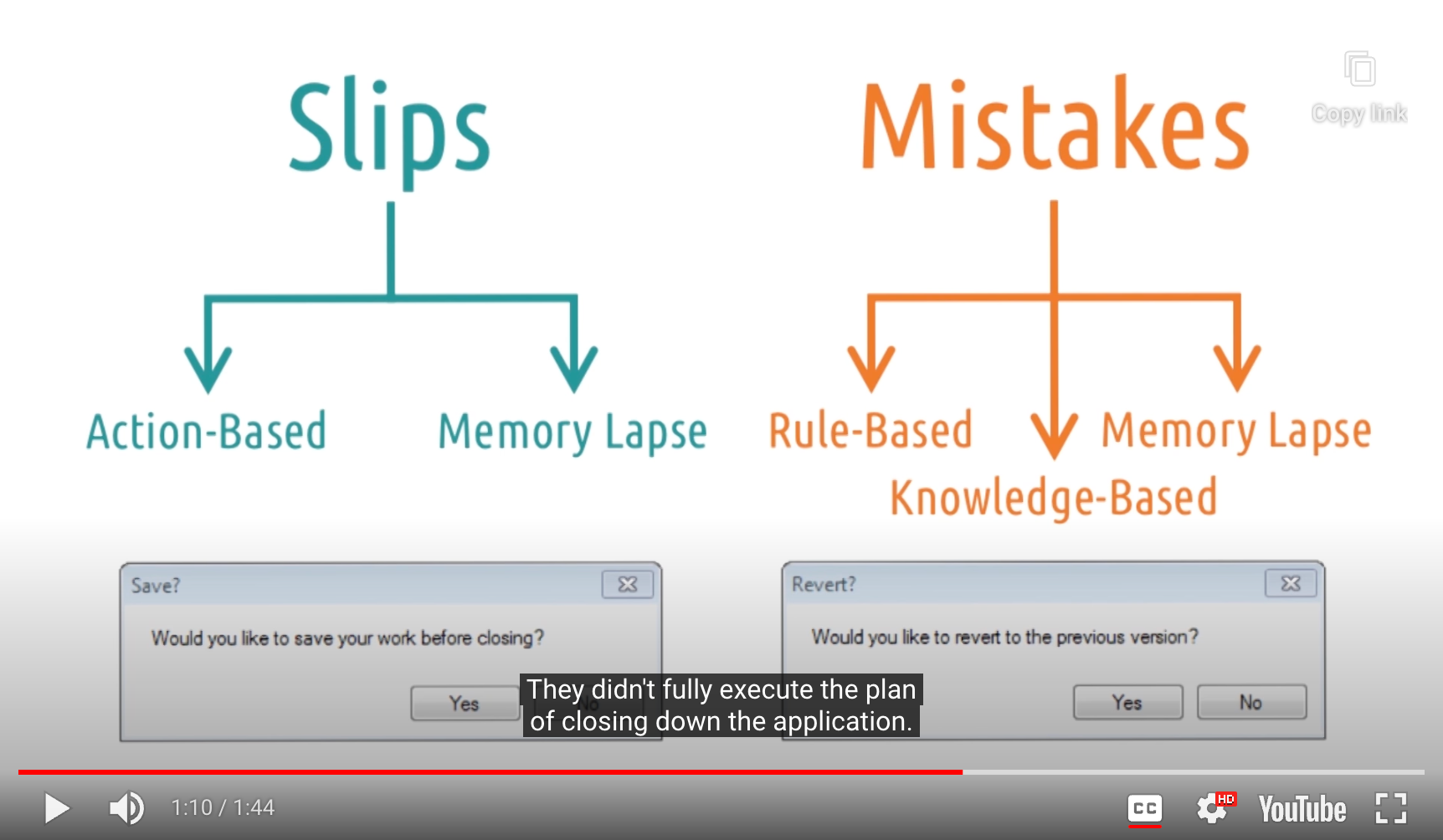
- Rule-Based : Doing the wrong thing
- 사용자가 현재 상태를 올바르게 판단(assess)했음에도, 그것에 근거에 잘못된 결정을 하는 경우
- 저장하고 싶다! -> revert에서 No라고 해야 될 것 같다 -> No 선택
- 사용자가 현재 상태를 올바르게 판단(assess)했음에도, 그것에 근거에 잘못된 결정을 하는 경우
- Knowledge-Based
- 사용자가 처음부터 현재 상태를 잘못 판단(assess)하는 경우
- 저장할게 있었나? -> 저장해야 하는 것 자체를 이해하지 못함
- 사용자가 처음부터 현재 상태를 잘못 판단(assess)하는 경우
- Memory Lapse : Forget to do the right thing
- 계획을 끝까지 수행해야 하지 못한 경우
- 이상한 메세지 창이 나왔네? -> 컴퓨터 전원을 꺼버려야 지
- 계획을 끝까지 수행해야 하지 못한 경우
우리의 목표는 위와 같은 일이 최대한 일어나지 않도록 올바른 디자인을 설계하는 것!
- 일관성(consistent) 있는 연습의 도움을 받아 Routine error(action-based slips)를 방지한다
- dialogue 디자인을 사용자가 친숙하도록 만든다
- 인터페이스가 작업 기억의 짐을 덜어주도록(off load) 설계해 Memroy Lapse error를 방지한다
- 좋은 심상(representation)을 통해 사용자가 올바른 mental model를 확립하도록 도와 Rule-Based / Knowledge-Based error를 방지한다
- error 들이 피할 수 없다면… Tolerance Principle에 따른다
- repercussions이 항상 가능하고 상태에 해를 끼치지 않도록 보장한다
Learned Helplessness

- User learn that there is no mapping between their input and the output they receive.
Learned Helplessness and Education
- 배우기를 거부하는 학생
- 그들이 배우기 위해 어떤 노력을 해도 성공하지 못했기 때문…
- They’ve learned to be helpless based on their past experiences
- 비유적으로 생각해보기
- 나 : User / 울고불고 난리치는 어린 아이 : Interface
- 우는 아이를 달래기 위해 어떤 피드백이 필요할까?
- Interface에 그와 같은 feedback을 어떻게 적용할 수 있을까?
- 나 : User / 울고불고 난리치는 어린 아이 : Interface

(요리할때 Learned Helplessness를 느끼신다는…)
Expert Blindspot

- I AM NOT MY USER
- ALLWAYS REMEMBER IT

- Repeat! I AM NOT MY USER